What is Ansible?
Table of Contents
Ansible is a simple open-source automation tool and engine for running Ansible playbooks. The big advantage of Ansible is that new users can easily learn all the functionalities and start using Ansible in short time. Ansible can adapt to any environment and automation is based on playbooks which are easy to understand and read. It is a tool that, unlike other atomization tools, offers simplicity. After a few months of pause, it’s easy to start where you left off.
Ansible advantages
Simplicity (Ansible uses simple syntax in a very understandable YAML format. No coding skills required).
Support for various technologies (Use Ansible to automate various platforms such as Windows, Linux, UNIX, physical, virtual and container environments.)
Agentless (Does not require the installation of special agents on machines.)
Dynamic Inventory Support (Ansible dynamically collects machines from various sources such as VMware, AWS and other).
Ansible uses cases
Provisioning (provision hosts of various functionalities. For example, if you want to test an application built in C#, Ansible installs and verifies all the necessary components required to perform successful application install.)
Configuration management (install, start and stop services, install and configure applications and operating systems, implement security settings,)
Application lifecycle management (when managing and deploying an application via Ansible Tower, teams can successfully manage the application lifecycle from deployment to production. Why care about moving application from one directory to another, adding a server xml file, and manually navigate to the web application when Ansible is doing job for you.)
Network Automation (Automate your network infrastructure with vendors like Cisco and Juniper.)
Security Standards (Analyze and change security setting via Ansible.)
Installation requirements
Ansible installation is easy and does not require many steps and software:
Control node – Python2.7+ or Python 3.5+, Ansible packages.
Managed nodes – Python2.7+ or Python 3.5, SSH enabled.
Does Ansible need to install agents on managed nodes?
Ansible does not require the installation of special agents on managed hosts. It uses OpenSSH or WinRM connection protocols. Ansible temporary installs modules on managed nodes and removes it when the process is complete.
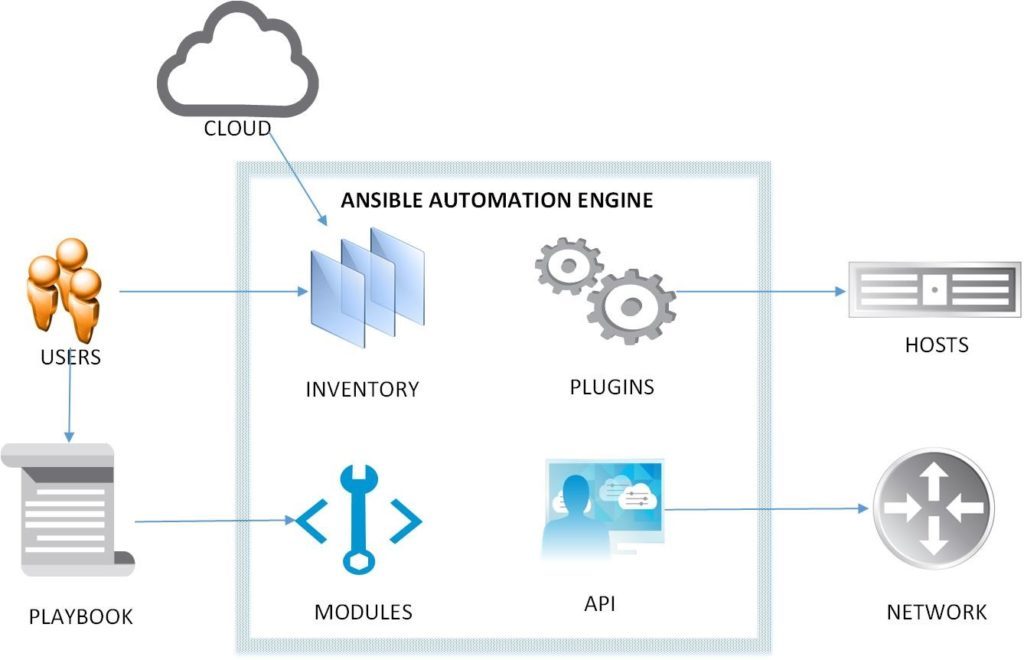
Architecture
Ansible architecture is very simple. There is control node and managed nodes. The control node can be installed on any machine such as your laptop, virtual machine, machine shared between administrators, etc. Managed nodes are hosts on which control node connects and perform changes. SSH keys are a recommended form of communication between control and managed nodes.
Managed hosts are listed in inventory file. Nodes can belong to specific group or just single hosts. Another important file in Ansible is a playbook, which includes some or all hosts from the inventory file, and plays that will run on managed nodes. Play executes a number of tasks – modules coded in Python or another programming language. Each module has a play role, for example, the copy module copies certain files or text to the remote host and assigns specific rights to users and groups. Tasks and plays are idempotent, which means they can be executed multiple times without consequences. There is exception when using module which work directly with shell.
For large enterprises there is enterprise solution – Red Hat Ansible Tower, an enterprise framework that provides a simple graphical interface and RESTful API for managing large enterprise environments.
Inventory: List of nodes managed through Ansible
APIs: APIs are used for Cloud public or private services
Modules: Executed directly on managed hosts. Modules can be installed packets, start and stop services, execute various commands and many more.
Plugins: Plugins extend the functionality of Ansible. For example, cache plugins can cache certain variables in order to avoid expensive collection of variables from remote nodes.
Ansible and DevOps
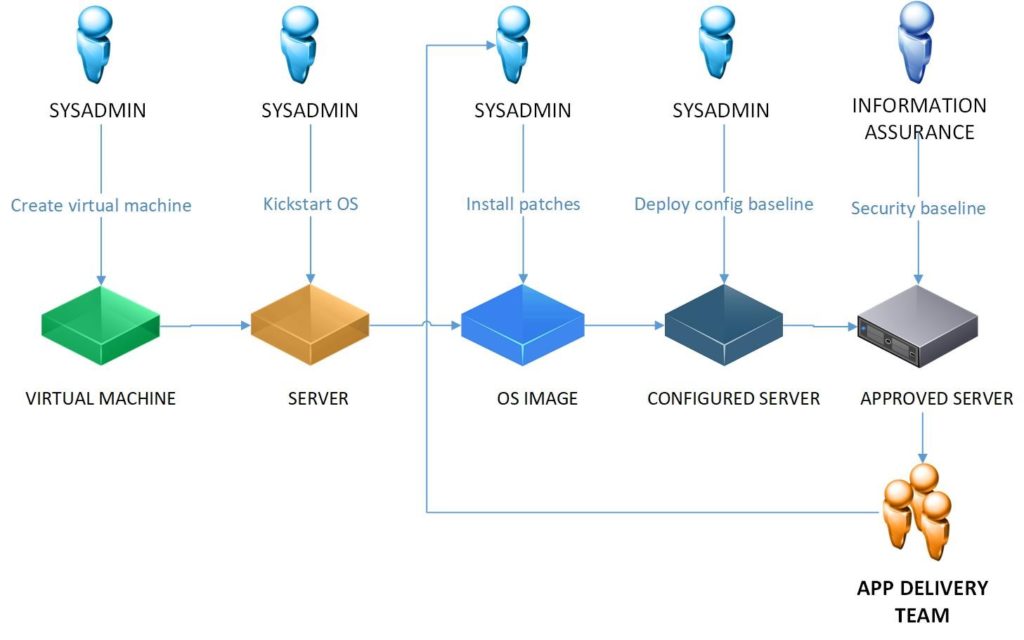
The manual installation and configuration of operating system or environment requires a large amount of hours that the system administrator has to spend. It is not a problem if it is done once or twice, but if process requires multiple repetitions of the same actions, some of which may end up in error, you can see the benefit of Ansible automation. The problem multiplies when other teams have to add their own configuration, for example security team has to install certain patches, application administrator has to install their applications, etc. The more teams have to touch the system the installation time and the configuration is extended.
Ansible provides a level of automation that allows you to deploy OS images on demand. Once the OS installation process is automated, automatization process for other teams becomes a trivial thing. Typical OS users such as developers and quality assurance engineers can safely run the correct OS configuration.
Ansible extensions
Ansible enables the ability to write custom modules that can be written in any language that supports JSON format such as Ruby, Python, Bash and many more. Dynamic inventories can also be created from any JSON-compliant data source. There are also many Python API modules that provide new ways of connecting to clients (SSH is the default).